Binary Search Algorithm.
- Calculate the middle index as (low + high) // 2.
- If the element at the middle index is equal to the target, return the index.
- If the element is greater than the target, update high to mid - 1 and repeat the search in the left half.
- If the element is smaller than the target, update low to mid + 1 and repeat the search in the right half.
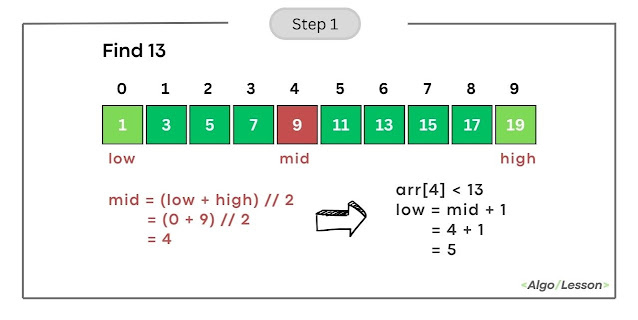
- Calculate mid as (low + high) // 2 = (0 + 9) // 2 = 4.
- Compare arr[mid] (element at index 4) with the target (13).
- Since arr[4] is less than 13, update low to mid + 1, making low = 5.
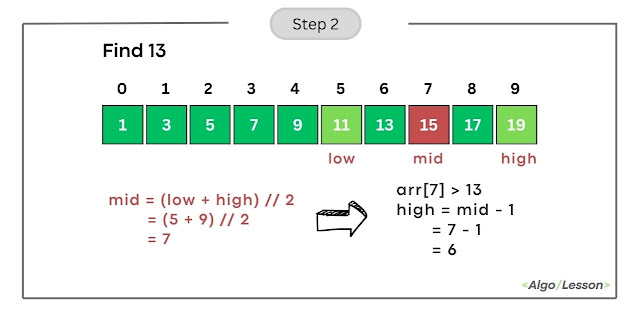
- Calculate mid as (low + high) // 2 = (5 + 9) // 2 = 7.
- Compare arr[mid] (element at index 7) with the target (13).
- Since arr[7] is greater than 13, update high to mid-1, making high = 6.
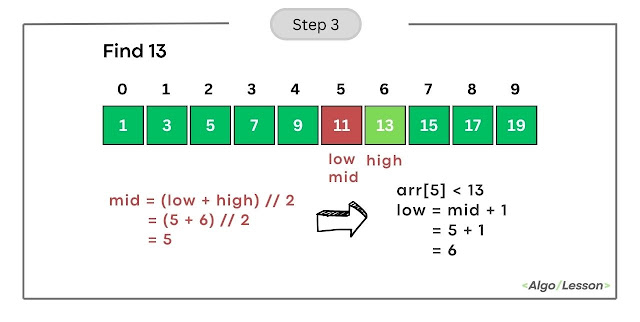
- Calculate mid as (low + high) // 2 = (5+ 6) // 2 = 5.
- Compare arr[mid] (element at index 5) with the target (13).
- Since arr[5] is less than 13, update low to mid + 1, making low = 6.
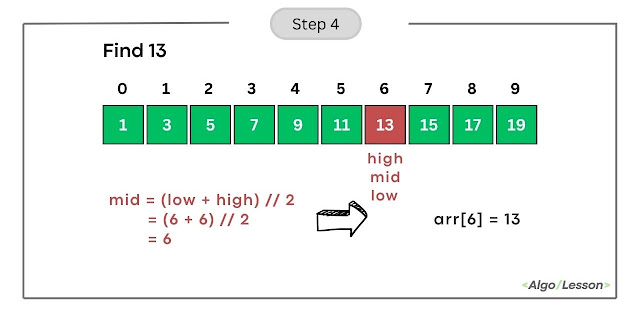
- Calculate mid as (low + high) // 2 = (6 + 6) // 2 = 6.
- Compare arr[mid] (element at index 6) with the target (13).
- Since arr[6] is equal to 13, we found the target. Return the index 6.
Python Program for Binary Search Using Iteration.
# Python code for Iterative Binary Search to find # target element from sorted array def binary_search(arr, target): low, high = 0, len(arr) - 1 while low <= high: mid = (low + high) // 2 mid_element = arr[mid] if mid_element == target: return mid elif mid_element < target: low = mid + 1 else: high = mid - 1 return -1 # Example sorted_array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] target_element = 6 result = binary_search(sorted_array, target_element) if result != -1: print(f"Element {target_element} is present at index {result}.") else: print(f"Element {target_element} is not present in the array.")
Element 6 is present at index 5.- Time Complexity: The time complexity of binary search is O(log n), where 'n' is the number of elements in the array.
- Space Complexity: The space complexity is O(1), indicating that the memory used by the algorithm remains constant regardless of the input size.
Python Program for Binary Search Using Recursion.
# Python code for Recursive Binary Search Algorithm def binary_search_recursive(arr, low, high, target): if low <= high: mid = (low + high) // 2 # Check if the target is present at the middle if arr[mid] == target: return mid # If the target is smaller, search in the left half elif arr[mid] > target: return binary_search_recursive(arr, low, mid - 1, target) # If the target is larger, search in the right half else: return binary_search_recursive(arr, mid + 1, high, target) else: # Target is not present in the array return -1 # Example usage: arr = [1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19] target = 13 result = binary_search_recursive(arr, 0, len(arr) - 1, target) if result != -1: print(f"Element {target} is present at index {result}.") else: print(f"Element {target} is not present in the array.")
Element 13 is present at index 6.- Time Complexity: The time complexity is O(log n) because, at each step, the search range is divided by 2.
- Space Complexity: The space complexity is O(log n) due to the recursive call stack.