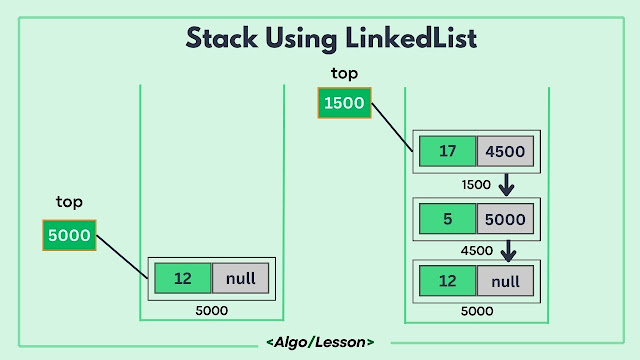
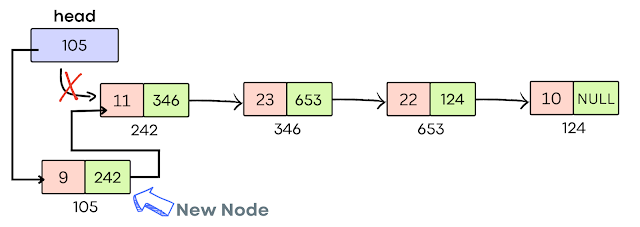
Stack Operations using Linked List.
// C++ code implementation for stack using linked list #include <iostream> using namespace std; // Node class for the linked list class Node { public: int data; Node* next; Node(int value) : data(value), next(nullptr) {} }; // Stack class using linked list class Stack { private: Node* top; public: Stack() : top(nullptr) {} // Push operation void push(int value) { Node* newNode = new Node(value); newNode->next = top; top = newNode; } // Pop operation void pop() { if (isEmpty()) { cout << "Stack is empty. Cannot pop." << endl; return; } Node* temp = top; top = top->next; delete temp; } // Check if the stack is empty bool isEmpty() { return top == nullptr; } // Display the top element of the stack void peek() { if (isEmpty()) { cout << "Stack is empty." << endl; return; } cout << "Top element: " << top->data << endl; } }; int main() { // Example usage of the stack Stack stack; // Push elements onto the stack stack.push(1); stack.push(2); stack.push(3); // Display the top element stack.peek(); // Pop an element stack.pop(); // Display the top element after pop stack.peek(); return 0; }
// Java code implementation for stack using Linked list public class Main { // Node class for the linked list static class Node { int data; Node next; Node(int value) { data = value; next = null; } } // Stack class using linked list static class Stack { private Node top; // Push operation void push(int value) { Node newNode = new Node(value); newNode.next = top; top = newNode; } // Pop operation void pop() { if (isEmpty()) { System.out.println("Stack is empty. Cannot pop."); return; } top = top.next; } // Check if the stack is empty boolean isEmpty() { return top == null; } // Display the top element of the stack void peek() { if (isEmpty()) { System.out.println("Stack is empty."); return; } System.out.println("Top element: " + top.data); } } public static void main(String[] args) { // Example usage of the stack Stack stack = new Stack(); // Push elements onto the stack stack.push(1); stack.push(2); stack.push(3); // Display the top element stack.peek(); // Pop an element stack.pop(); // Display the top element after pop stack.peek(); } }
# Python code implementation of stack using linked list class Node: def __init__(self, value): self.data = value self.next = None class Stack: def __init__(self): self.top = None # Push operation def push(self, value): new_node = Node(value) new_node.next = self.top self.top = new_node # Pop operation def pop(self): if self.is_empty(): print("Stack is empty. Cannot pop.") return self.top = self.top.next # Check if the stack is empty def is_empty(self): return self.top is None # Display the top element of the stack def peek(self): if self.is_empty(): print("Stack is empty.") return print("Top element:", self.top.data) # Example usage of the stack stack = Stack() # Push elements onto the stack stack.push(1) stack.push(2) stack.push(3) # Display the top element stack.peek() # Pop an element stack.pop() # Display the top element after pop stack.peek()
// C-Sharp code implementation for stack using linked list using System; // Node class for the linked list public class Node { public int Data; public Node Next; public Node(int value) { Data = value; Next = null; } } // Stack class using linked list public class Stack { private Node top; // Push operation public void Push(int value) { Node newNode = new Node(value); newNode.Next = top; top = newNode; } // Pop operation public void Pop() { if (IsEmpty()) { Console.WriteLine("Stack is empty. Cannot pop."); return; } top = top.Next; } // Check if the stack is empty public bool IsEmpty() { return top == null; } // Display the top element of the stack public void Peek() { if (IsEmpty()) { Console.WriteLine("Stack is empty."); return; } Console.WriteLine("Top element: " + top.Data); } } class Program { static void Main() { // Example usage of the stack Stack stack = new Stack(); // Push elements onto the stack stack.Push(1); stack.Push(2); stack.Push(3); // Display the top element stack.Peek(); // Pop an element stack.Pop(); // Display the top element after pop stack.Peek(); } }
Top element: 3
Top element: 2
Benefits of Stack Implementation using LinkedList.
- Dynamic Memory Allocation: Linked lists allow dynamic memory allocation, accommodating a varying number of elements without predefining a fixed size, providing flexibility.
- Efficient Insertions and Deletions: Push and pop operations in linked lists execute in constant time, making them efficient for stack implementations.
- Simplicity and Ease of Use: Implementing a stack using a linked list is relatively straightforward and easy to understand, aiding in code readability and maintenance.
- No Memory Wastage: Linked lists utilize memory efficiently by allocating space only as needed for elements, preventing memory wastage.