1. What is HTML?
2. What does HTML stand for?
3. What is the latest version of HTML?
4. What are the new features of HTML5?
- Semantic Elements: New semantic elements like `<header>`, `<footer>`, `<article>`, `<section>`, and `<nav`> provide clearer document structure.
- Audio and Video Support: Native support for embedding audio and video content using the `<audio>` and `<video>` elements, eliminating the need for third-party plugins like Flash.
- Canvas Element: The `<canvas>` element allows dynamic rendering of graphics, enabling the creation of interactive and animated content directly within the browser.
- New Form Input Types: Additional form input types such as `<email>`, `<url>`, `<tel>`, `<number>`, `<date>`, and more enhance the user experience and provide better input validation.
- Local Storage: Introducing the `localStorage` object enables web applications to store data locally on the user's device, improving offline capabilities and performance.
- Web Workers: Web Workers allow the execution of scripts in the background, enabling parallel processing and improved performance without affecting the main user interface.
- Geolocation API: The Geolocation API provides native support for obtaining the user's geographical location, enabling location-based services in web applications.
- Offline Web Applications: HTML5 includes features like the Application Cache and the `manifest` attribute, allowing web applications to work offline and providing a better user experience.
- New Structural Elements: Introduction of elements like `<article>`, `<aside>`, `<mark>`, `<progress>`, `<output>`, and more for better document structure and semantics.
- Drag-and-Drop Support: Native support for drag-and-drop functionality simplifies the implementation of interactive interfaces and content manipulation.
- WebSocket: The WebSocket API enables bidirectional communication between the browser and the server, facilitating real-time updates and data exchange.
- Web Storage: Alongside `localStorage`, HTML5 also introduces `sessionStorage` for storing session-specific data on the client side.
5. Explain the Basic Structure of HTML.
- Document Type Declaration: The <!DOCTYPE html> declaration at the beginning of the HTML document defines the document type and version. It helps browsers to render the page correctly.
- HTML Root Element: The <html> element serves as the root element of the HTML document. It wraps the entire content and includes language attributes such as lang to specify the language of the document.
- Head Section: The <head> element contains metadata about the document, such as the title, character set, linked stylesheets, and scripts.
- Body Section: The <body> element encloses the main content of the HTML document, including text, images, links, forms, and other elements that make up the visible part of the webpage.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /> <title>My Webpage</title> <!-- Additional meta tags, stylesheets, and scripts can be added here --> </head> <body> <!--This section will be visible to the end user--> </body> </html>
6. What is the purpose of <!DOCTYPE> declaration?
7. Difference Between HTML and XHTML.
HTML (HyperText Markup Language):
- Nature: HTML is more forgiving and lenient in terms of syntax rules.
- Parsing: Browsers are forgiving and can render a page even with syntax errors.
- Tags: Case sensitivity is not strict, and tags can be written in uppercase or lowercase.
- Self-Closing Tags: Self-closing tags are optional (e.g., `<img>` or `<br>`).
XHTML (eXtensible HyperText Markup Language):
- Nature: XHTML is stricter and follows XML syntax rules.
- Parsing: Browsers are less forgiving; a small syntax error can break the rendering.
- Tags: Case sensitivity is strict, and all tags must be written in lowercase.
- Self-Closing Tags: Self-closing tags are mandatory (e.g., `<img />` or `<br />`).
8. What is semantic HTML? Can you give examples?
- <header>: Represents the header of a section or page.
- <nav>: Defines a navigation menu.
- <article>: Represents an independent, self-contained piece of content.
- <section>: Defines a section in a document.
- <aside>: Represents content tangentially related to the content around it.
- <footer>: Represents the footer of a section or page.
- <figure> and <figcaption>: Used to encapsulate media and its caption.
9. Explain the difference between Block-Level Elements and Inline Elements.
10. What is the purpose of <head> element in HTML?
11. What is the use of <meta> elements in HTML?
12. What is the meaning of initial-scale=1.0 in HTML?
13. What are attributes in HTML?
14. What is the purpose of 'alt' attribute in <img> tag?
15. How to create a Hyperlink in HTML?
<a href="https://www.example.com">Visit Example.com</a>
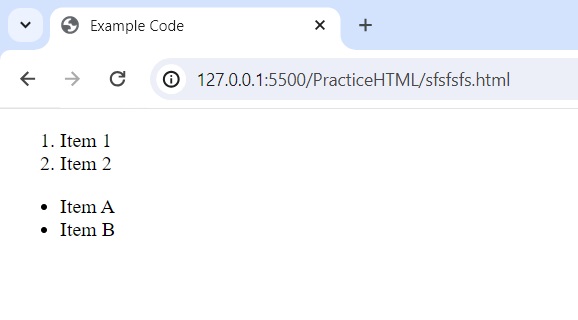
16. What is the difference Between <ol> and <ul> element?
- <ol> (Ordered List): Represents a list where items are ordered or numbered sequentially.
- <ul> (Unordered List): Represents a list where items are not ordered and are typically displayed with bullets.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /> <title>Example Code</title> </head> <body> <ol> <li>Item 1</li> <li>Item 2</li> </ol> <ul> <li>Item A</li> <li>Item B</li> </ul> </body> </html>
- Example: <p>, <a>, <img>
- Example: <p>This is a paragraph.</p>
18. Explain the purpose of <iframe> tag.
19. What is the importance of the lang attribute in <HTML> tag?
20. How do you embed audio and video in HTML?
<audio controls> <source src="audio.mp3" type="audio/mp3"> Your browser does not support the audio tag. </audio> <video width="320" height="240" controls> <source src="video.mp4" type="video/mp4"> Your browser does not support the video tag. </video>
21. What is the use of the HTML5 Canvas element?
22. What are HTML Forms?
23. What is the purpose of the 'required' attribute in a Form?
24. What is the role of <label> element in a form?
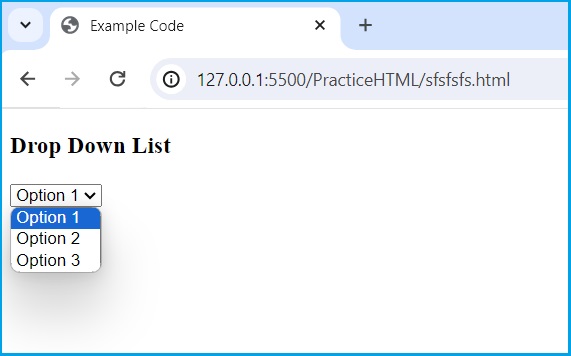
25. How do you create a dropdown list in HTML?
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /> <title>Example Code</title> </head> <body> <h3>Drop Down List</h3> <select> <option value="option1">Option 1</option> <option value="option2">Option 2</option> <option value="option3">Option 3</option> </select> </body> </html>
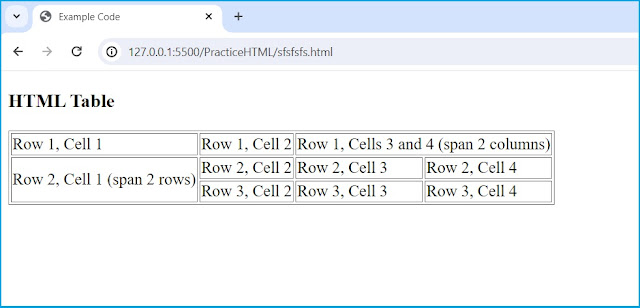
26. What is the purpose of the 'colspan' and 'rowspan' attributes in a table?
- colspan: Specifies the number of columns a table cell should span horizontally.
- rowspan: Specifies the number of rows a table cell should span vertically.
28. Explain the importance of the 'rel' attribute in the <a> tag.
29. Explain the difference between cookies and local storage.
- Small pieces of data are stored on the client side.
- Sent with every HTTP request, impacting performance.
- Typically limited to 4KB in size.
- Has an expiration date and can be set for sessions or persisted.
- Used for client-server communication and maintaining user sessions.
- Larger storage capacity (typically 5-10MB per domain).
- Not automatically sent with HTTP requests, reducing overhead.
- Persists even after the browser is closed.
- Accessed via the `localStorage` object in JavaScript.
- Used for client-side data storage, improving performance for some scenarios.
30. How To Disable Form Elelemt in HTML?
<input type="text" name="username" disabled>
31. Explain the concept of HTML Microdata.
32. What is a tooltip in HTML?
33. Difference between <div> and <span> tag.
- <div>: A block-level element used for grouping and structuring content. It typically starts on a new line and takes up the full width of its container.
- <span>: An inline element used for applying styles or scripting to a specific portion of text within a larger block. It does not create a new block and only takes up as much width as its content.
34. How to add a comment in HTML?
<!-- This is a comment in HTML --> <p>This is a paragraph.</p>