Stack Class in Java.
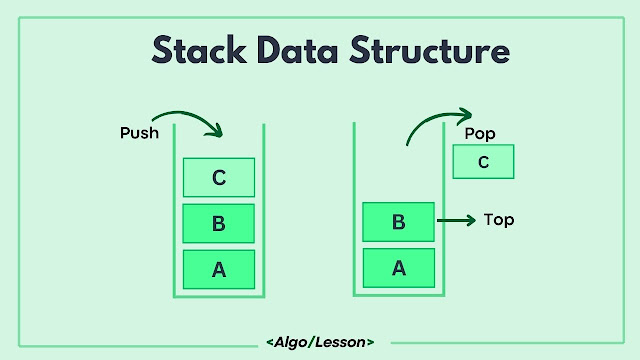
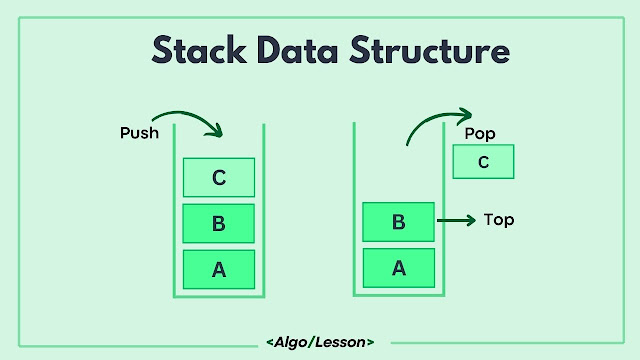
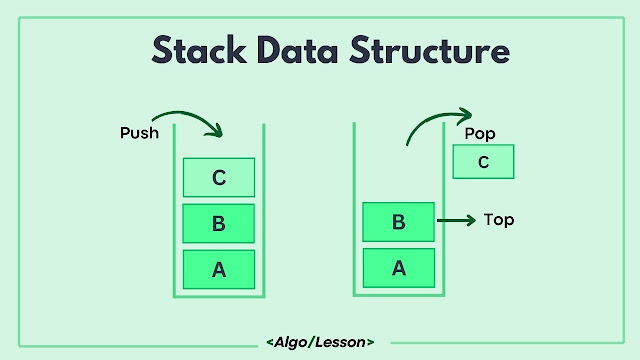
List of Basic Stack Operations:
- push(element): Adds an element to the top of the stack.
- pop(): Removes and returns the top element from the stack.
- peek(): Returns the top element without removing it.
- isEmpty(): Checks if the stack is empty.
- search(element): Searches for an element in the stack and returns its position.
How To Use Stack Class in Java?
// Java Stack Class Implementation code import java.util.Stack; public class StackOperationsExample { public static void main(String[] args) { // Creating a stack of integers Stack<Integer> myStack = new Stack<>(); // Pushing elements onto the stack myStack.push(10); myStack.push(20); myStack.push(30); // Accessing the top element without removing it (peek) int topElement = myStack.peek(); System.out.println("Top element: " + topElement); // Popping the top element int poppedElement = myStack.pop(); System.out.println("Popped element: " + poppedElement); // Checking if the stack is empty boolean isEmpty = myStack.empty(); System.out.println("Is stack empty? " + isEmpty); // Determining the size of the stack int stackSize = myStack.size(); System.out.println("Size of stack: " + stackSize); // Search for an element in the stack int searchElement = 20; int position = myStack.search(searchElement); if (position != -1) { System.out.println("Element " + searchElement + " found at position: " + position); } else { System.out.println("Element " + searchElement + " not found in the stack"); } } }
Top element: 30
Popped element: 30
Is stack empty? false
Size of stack: 2Element 20 found at position: 1
- Time Complexity: push(), pop(), peek(), empty(), size() have constant time O(1) complexity. These operations generally perform in constant time regardless of the number of elements in the stack.
- Space Complexity: The space complexity of the Stack in Java is O(n) where n is the number of elements in the stack.