In our previous post, we discussed Merge Sort Algorithm and we know that Merge Sort Algorithm has O(nlogn) time complexity in the worse case and it is an in-place algorithm with O(n) space complexity.
Here in this post, we are going to discuss the Quick Sort Algorithm which is a recursive algorithm whose average case time complexity is O(nlogn) and worse case time complexity is O(n^2) but unlike merge sort, it is an in-place algorithm with O(1) space complexity.
Note: Quick Sort has O(n^2) time complexity in the worse case but it is much more efficient in practical scenarios that we can ignore the worse case running time by using a randomized version of Quick Sort. Sort function which is available for us by most of the programming language libraries is implemented using Quick Sort.(alert-success)
Working of Quick Sort Algorithm.
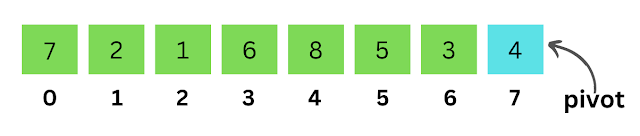
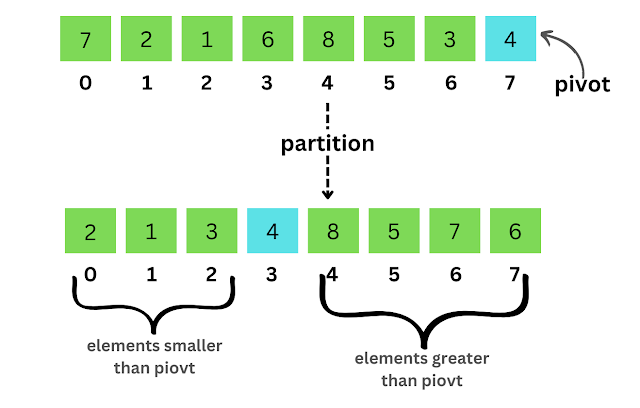
In the Quick Sort algorithm, we first select one element from the given array and there are no strict rules for picking this element we can pick any element. Now let's say we picked the last element and consider this as a pivot of our algorithm.
Our next step is that we need to re-arrange the given array such that all the elements smaller than the pivot are moved towards the left side of the pivot and all the elements greater than the pivot are moved towards the right of the pivot. This process is known as the partitioning of the given array. All the rearrangements are happening in the original array only.
Once the partitioning is done for the given array we can break our problem into two sub-problem where we need to sort the segment of the array present on the left side of the pivot and we need to sort the segment of the array present on the right side of the pivot. We repeat this process recursively until we are left with no or only one element.
Algorithm of Quick Sort.
QuickSort(Array[], start, end)
{
if(start >= end) return;
pindex = partition(Array[], start, end);
QuickSort(Array[], start, pindex-1);//Before pivot
QuickSort(Array[], pindex+1, high);//After pivot
}(alert-passed)
Working of Partition Algorithm.
Let's say the last element of the array is our pivot element and by partitioning, we will move all smaller elements to the left side of the pivot and all greater elements to the right side of the pivot. By using this algorithm each time we are placing the pivot element to its correct location in our array.
Algorithm of Partition.
Partition(Array[], start, end)
{
pivot = Array[end];
pindex = start;
for(i = start to end -1)
{
if(Array[i] <= pivot)
{
swap(Array[i], Array[pindex]);
pindex = pindex+1;
}
}
swap(Array[pindex], Array[end]);
return pindex;
}(alert-passed)
C++ Code Implementation of Quick Sort Algorithm.
//C++ Code for Quick Sort Algorithm #include<iostream> using namespace std; /* Partition function taken last element as a pivot and place the pivot at its correct location in the given array by arrranging all smaller element to left side of pivot and all greater element to right side of pivot. */ int partition(int arr[], int start, int end){ //pivot element int pivot = arr[end]; int pindex = start; for(int i = start; i < end; i++){ //current element is smaller than or equal to pivot if(arr[i] <= pivot){ swap(arr[i], arr[pindex]); pindex = pindex+1; } } swap(arr[pindex], arr[end]); return pindex; } //Recursive Quick Sort function void quickSort(int arr[], int start, int end){ //base case if(start >= end) return; /*pindex is partitioning index or it is the correct position of pivot element*/ int pindex = partition(arr, start, end); quickSort(arr, start, pindex-1); //sorting before pivot quickSort(arr, pindex+1, end); //sorting after pivot } int main(){ int arr[] = {7, 2, 1, 6, 8, 5, 3, 4}; //Size of given array int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]); cout<<"Array Before Sorting: "; for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){ cout<<arr[i]<<" "; } quickSort(arr, 0, n-1); cout<<"\nArray After Sorting: "; for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){ cout<<arr[i]<<" "; } }
Array Before Sorting: 7 2 1 6 8 5 3 4 Array After Sorting: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
- Time Complexity: The average case time complexity of the QuickSort algorithm is O(nlogn) and the worst case time complexity is O(n^2).
- Space Complexity: The space complexity of the Quick Sort algorithm is O(1) because of all the operations of and the arrangement was happing in the same given array.







.png)