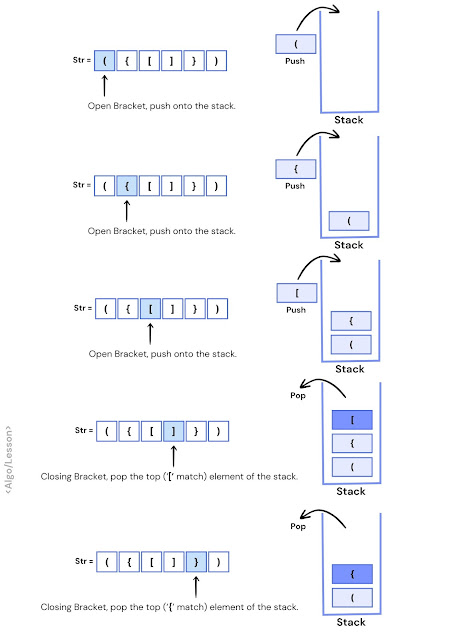
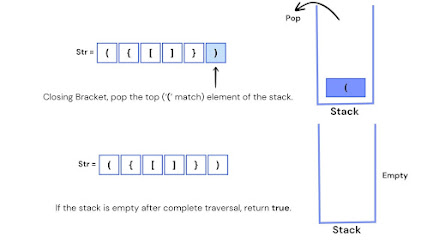
Check Valid Balanced Parenthesis Using Stack.
Algorithm Steps to Validate Parenthesis:
- If the character is an opening parenthesis ('(', '{', '['), push it onto the stack.
- If the character is a closing parenthesis (')', '}', ']') then check if the stack is empty then return false (unbalanced) else pop the top element and check if it matches with the closing parenthesis.
- If the closing parenthesis does not match with the top element of the stack then return false.
Example Illustration.
Below is the code implementation of the above approach:// C++ code implementation to check balanced parenthesis #include<iostream> #include<stack> using namespace std; //function to check balance parenthesis bool validParenthesis(string str){ stack<char> st; for(int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++){ //opening parenthesis, push into the stack if(str[i] == '{' || str[i] == '[' || str[i] == '(') { st.push(str[i]); }else if(str[i] == '}' || str[i] == ']' || str[i] == ')') { //empty stack if(st.empty()) return false; //check if stack top contain a matching opening bracket //pop the top element if matching is found if((st.top() == '{' && str[i] == '}') || (st.top() == '[' && str[i] == ']') || (st.top() == '(' && str[i] == ')')) { st.pop(); } else{ return false; } } } //stack is empty after complete iteration if(st.empty()) return true; return false; } int main() { string str = "[{(){()}}]"; if(validParenthesis(str)){ cout<<"Balance Parenthesis"<<endl; }else{ cout<<"Unbalance Parenthesis"<<endl; } return 0; }
// Java Code Implementation to check balanced parenthesis import java.util.Stack; public class ParenthesisChecker { public static boolean isValidParenthesis(String str) { Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>(); //push the char in stack if they are opening brackets for (char ch : str.toCharArray()) { if (ch == '{' || ch == '[' || ch == '(') { stack.push(ch); } else if (ch == '}' || ch == ']' || ch == ')') { if (stack.isEmpty()) return false; //pop the top element if matching bracket is found char top = stack.pop(); if ((top == '{' && ch == '}') || (top == '[' && ch == ']') || (top == '(' && ch == ')')) { continue; } else { return false; // Mismatched brackets } } } return stack.isEmpty(); } public static void main(String[] args) { String str = "[{(){()}}]"; if (isValidParenthesis(str)) { System.out.println("Balanced Parenthesis"); } else { System.out.println("Unbalanced Parenthesis"); } } }
# Python code to check balanced parenthesis def is_valid_parenthesis(s): stack = [] for char in s: # checking for open brackets if char in '{[(': stack.append(char) # checking for closing brackets elif char in '})]': if not stack: return False # pop the top char from stack if matching pair is found top = stack.pop() if (top == '{' and char == '}') or (top == '[' and char == ']') or (top == '(' and char == ')'): pass else: return False # Mismatched brackets return not stack # Example usage parenthesis_str = "[{(){()}}]" if is_valid_parenthesis(parenthesis_str): print("Balanced Parenthesis") else: print("Unbalanced Parenthesis")
// C# code to check balanced parenthesis using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class ParenthesisChecker { static bool IsValidParenthesis(string str) { Stack<char> stack = new Stack<char>(); foreach (char ch in str) { // push the char in stack if it is opening bracket if (ch == '{' || ch == '[' || ch == '(') { stack.Push(ch); } // pop the top char from stack if it is matching pair of closing bracket else if (ch == '}' || ch == ']' || ch == ')') { if (stack.Count == 0) return false; char top = stack.Pop(); if ((top == '{' && ch == '}') || (top == '[' && ch == ']') || (top == '(' && ch == ')')) { continue;// Matching brackets, continue } else { return false; // Mismatched brackets } } } return stack.Count == 0; } static void Main() { string str = "[{(){()}}]"; if (IsValidParenthesis(str)) { Console.WriteLine("Balanced Parenthesis"); } else { Console.WriteLine("Unbalanced Parenthesis"); } } }
Balanced Parenthesis
- Time Complexity: The algorithm iterates through each character in the expression once, resulting in a time complexity of O(n), where n is the length of the expression.
- Space Complexity: The space complexity is O(n), where n is the length of the expression. This is due to the stack storing opening parentheses, and in the worst case, the stack may contain all opening parentheses before encountering the corresponding closing ones.
Check Balanced Parenthesis Without Using Stack.
Algorithm Steps:
- If ch is an opening parenthesis ('(', '{', '[') then increase the value of i by 1 and replace the character at index i in the expression with the opening bracket.
- If ch is a closing parenthesis (')', '}', ']') check if i is greater than or equal to 0. Check if the current closing bracket matches the corresponding opening bracket at index i: If yes, decrement i by 1 else returns false.
// C++ code to check balance parenthesis without stack #include<iostream> using namespace std; //function to check parenthesis is balance or not bool validParenthesis(string str) { // Initialize an index variable for tracking the top of the stack int i = -1; for(int j = 0; j < str.size(); j++) { if(str[j] == '{' || str[j] == '[' || str[j] == '('){ // Increment counter for opening parenthesis i++; // Replace ith character with the opening bracket str[i] = str[j]; } else{ if(i >= 0 && ((str[i] == '(' && str[j] == ')') || (str[i] == '{' && str[j] == '}') || (str[i] == '[' && str[j] == ']'))) { // Decrement counter for matching closing parenthesis i--; } else { return false; } } } // -1 indicate that stack is empty (balanced parenthesis) if(i == -1) return true; return false; } int main() { string str = "({[][{]})"; if(validParenthesis(str)){ cout<<"Balance Parenthesis"<<endl; }else{ cout<<"Unbalance Parenthesis"<<endl; } return 0; }
// Java code implementation to check valid parenthesis import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { // Function to check if parentheses are balanced static boolean validParenthesis(String str) { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); int i = -1; for (int j = 0; j < str.length(); j++) { char ch = str.charAt(j); if (ch == '{' || ch == '[' || ch == '(') { i++; sb.append(ch); } else { if (i >= 0 && ((sb.charAt(i) == '(' && ch == ')') ||
(sb.charAt(i) == '{' && ch == '}') || (sb.charAt(i) == '[' && ch == ']'))) { i--; } else { return false; } } } return i == -1; } public static void main(String[] args) { String str = "({[][{]})"; if (validParenthesis(str)) { System.out.println("Balanced Parenthesis"); } else { System.out.println("Unbalanced Parenthesis"); } } }
# Python program to validate parenthesis def validParenthesis(s): i = -1 for j in range(len(s)): if s[j] in ['{', '[', '(']: i += 1 s = s[:i + 1] + s[j] else: if i >= 0 and ((s[i] == '(' and s[j] == ')') or (s[i] == '{' and s[j] == '}') or (s[i] == '[' and s[j] == ']')): i -= 1 else: return False return i == -1 str_value = "({[][{]})" if validParenthesis(str_value): print("Balanced Parenthesis") else: print("Unbalanced Parenthesis")
// C# code to check valid balanced parenthesis using System; class Program { // Function to check if parentheses are balanced static bool ValidParenthesis(string str) { int i = -1; char[] sb = new char[str.Length]; for (int j = 0; j < str.Length; j++) { char ch = str[j]; if (ch == '{' || ch == '[' || ch == '(') { i++; sb[i] = ch; } else { if (i >= 0 && ((sb[i] == '(' && ch == ')') || (sb[i] == '{' && ch == '}')
|| (sb[i] == '[' && ch == ']'))) { i--; } else { return false; } } } return i == -1; } static void Main() { string str = "({[][]})"; if (ValidParenthesis(str)) { Console.WriteLine("Balanced Parenthesis"); } else { Console.WriteLine("Unbalanced Parenthesis"); } } }
Unbalanced Parenthesis
- Time Complexity: Time complexity of the above solution in O(n) where n is the length of the given expression.
- Space Complexity: Space complexity is O(1) if it is allowed to modify the existing string otherwise, it will be O(n).